

Cons: Less personalization, application flexibility That separates the OS from user data and allows admins to store that data on a lower-cost device. User configuration settings and data are stored on separate hardware that's accessible remotely, such as a network share. This setup also means there's less storage to deal with. If the same instance happened with a persistent desktop, that desktop user's credentials or other sensitive data could be compromised. Plus, if the image is hacked or compromised, you can simply reboot desktops back to a clean state. Users can't alter desktop settings or install their own applications, making the image more secure. Since nonpersistent desktops are built from a master image, it's easier for administrators to patch and update the image, back it up quickly and deploy company-wide applications to all end users. Pros: Image manageability, greater security, less storage At the end of a session, the desktop reverts to its original state and the user receives a fresh image the next time he logs in. When users access a nonpersistent desktop, none of their settings or data is saved once they log out. Recently, more storage products and features have been made available for persistent desktops, eliminating some of the storage constraints that kept administrators away from persistent desktop virtualization in the past.Īn additional concern is that it's more complex to manage numerous diverse images than a master image, which can be altered and updated in one stroke. Storage for persistent desktops is usually a separate logical drive, so it's integrated with the underlying VM, while the actual user data is stored on the desktop itself. User settings and customizations are stored separately as user layers that the VDI applies to the golden image desktop during the delivery of the VM. The golden image, also known as a master image, is one or several stripped-down desktops that contain only essential applications and data. All those individual, customized disk images require more storage capacity than a single golden image does with nonpersistent desktops.
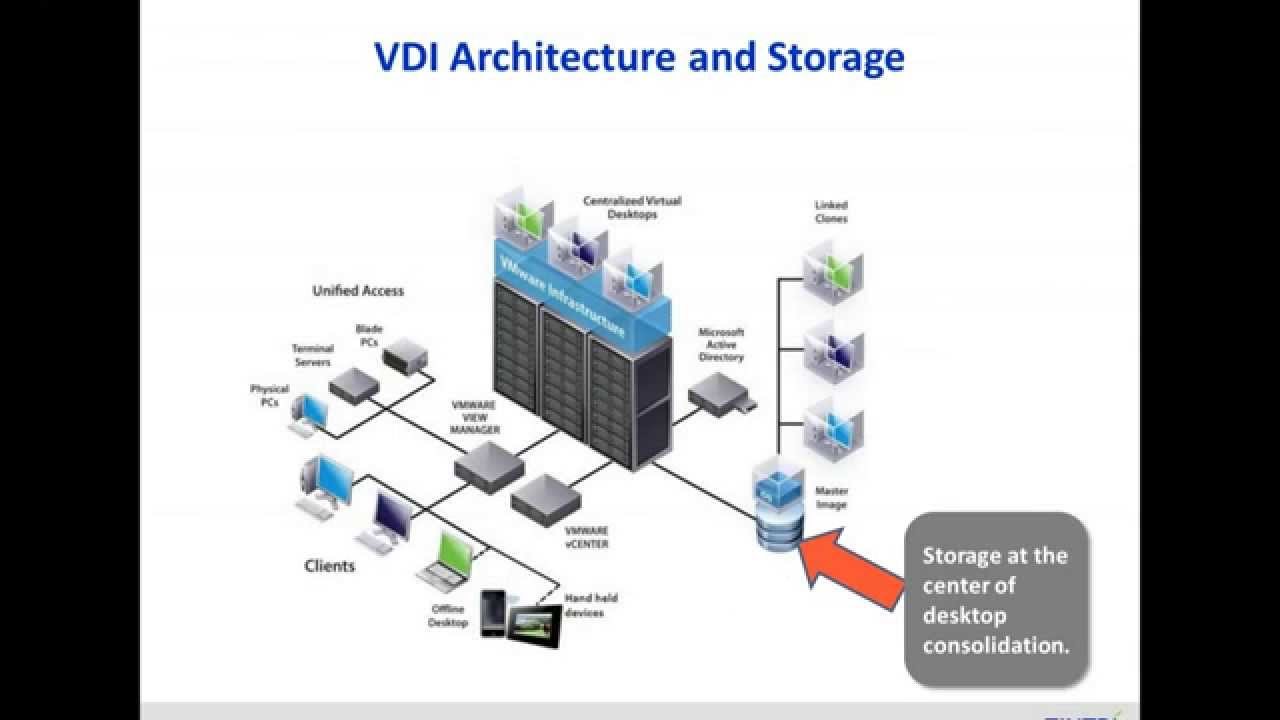
Storage is a major concern with persistent VDI. Cons: Storage requirements and image management Rather than re-engineering your desktops when you move to VDI, you can stick with a one-to-one setup.

Plus, persistent VDI is basically the same setup you had with your physical desktops, making it easier for many admins to manage. That aspect of persistent desktops tends to help users embrace VDI more easily because it provides the same consistency and customizations that typical desktops include. It's easier to personalize persistent desktops because users can access their own data, shortcuts and files from the same desktop every time they log in. Download this entire guide for FREE now! Pros: Customization and familiarity


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
